1.What is the role of a Big Data Developer?
A Big Data Developer is the one
who develops, maintains, tests, and evaluates Big Data solutions within
organizations. He designs Big Data solutions using HBase and Hive. Moreover, a
Big Data Developer has to design, construct, install, test, and maintain highly
scalable Data Management Systems. He should be able to use HCatalog with Hive
Managing and deploy HBase.
A Big Data Developer is also
expected to manage Hadoop cluster with all included services like developing
dataset processes for data modelling, mining, production and integrating new
Data Management technologies and software engineering tools into existing
structures.
2. What are the core components that are utilized
in Hadoop?
The core components used in
Hadoop include:
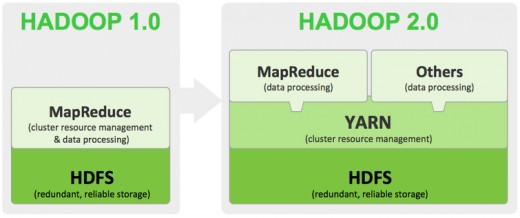
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
Hadoop Map Reduce
YARN
What are some of the different
modes used in Hadoop?
Some of the different modes used
in Hadoop are:
Standalone Mode, also known as
Local Mode
Pseudo – Distributed Mode
Fully – Distributed Mode
3. List the common input formats
used in Hadoop.
Some of the common input formats
used in Hadoop include:
Key Value Input Format
Sequence File Input Format
Text Input Format
What is the procedure to recover
a Name Node when it is slow?
In order to recover a Name Node,
following steps need to be carried out:
Using the file system metadata
replica FsImage start a new Name Node.
Configure different Data Nodes
along with the clients in order to make them recognize the newly initiated Name
Node.
As soon as the new Name Node has
completed the checkpoint using FsImage, it will start helping the clients. This
is achieved when FsImage has received enough amount of block reports from Data
Nodes.
Differentiate between NAS and
HDFS
In the case of HDFS, data storage
is achieved in the form of data blocks within local drivers. On the contrary,
data storage in NAS is achieved in the form of dedicated hardware.
HDFS works with the help of
machines in the form of clusters while NAS works with the help of individual
machines.
Data dismissal is a common issue
in case of HDFS; no such problem is encountered while using NAS.
3.What is the purpose of using
Hadoop for Big Data Analytics?
Hadoop is mainly used for Big
Data Analysis for the following benefits:
Storage
Processing
Data Collection
Ease of dealing with varied
structured, semi-structured and unstructured data
Cost-benefit
Name the components of HDFS and
YARN respectively
The components of HDFS include:
Name Node
Data Node or Slave node
The components of YARN include:
Resource Manager
Node Manager
4.What do you mean by Data
Processing?
Data Processing is the final step
of Big Data Solutions. In this step, with the help of different processing
frameworks, the data is processed. Various processing frameworks used are Pig, Map
Reduce, Spark, etc.
What do you understand by the
term Data Storage?
Data Storage is the next step in
Big Data Solutions. In this step, the data is extracted from the first step is
stored in HDFS or NoSQL database, also known as HBase. The HDFS storage is
widely used for sequential access. On the contrary, HBase is used for random
read or write access.
Explain the first step in Big
Data Solutions.
Data Ingestion is the first step
of Big Data Solutions. This step refers to the extraction of data from
different sources. Different sources data could include CRM, for instance,
Salesforce; RDBMS such as MySQL, various Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
such as SAP other with other log files, social media feeds, documents, papers,
etc. All the data that is extracted is then stored in HDFS.
5. What are the three steps
involved in Big Data?
The three essential steps
involved in Big Data are:
Data Ingestion
Data Storage
Data Processing
6.How does Big Data help in
increasing business revenue?
Big Data has been widely used by
a number of organizations in order to increase their business revenue. It is
done by helping organizations to distinguish themselves from other competitors
in the market. Big Data provides organizations with customized suggestions and
recommendations through a series of predictive analysis. Big Data also allows
organizations to release new products in accordance with the needs of the
customer and their preferences. All these factors contribute to the increase in
revenue of a particular business.
LEARN LATEST INTERVIEW QUESTION & ANSWERS
7. What is the connection between Hadoop and Big
Data?
Hadoop and Big Data are nearly
equivalent terms with respect to each other. However, with the ascent of Big
Data, Hadoop has also been commonly used. It is a system, which has practical
experience in Big Data and also performs additional tasks. Experts can utilize
this system in order to break down Big Data and help organizations to make
further decisions.
List the five important V’s of Big Data.
The five important V’s of Big
Data are:
Value – It refers to changing
data into value, which allows businesses to generate revenue.
Velocity – Any data growing at an
increasing rate is known as its variety. Social media is an important factor
contributing to the growth of data.
Variety – Data can be of
different types such as texts, audios, videos, etc. which are known as variety.
Volume – It refers to the amount
of any data that is growing at an exponential rate.
Veracity – It refers to the
uncertainty found in the availability of data. It mainly arises due to the high
demand for data which results in inconsistency and incompleteness.
What do you mean by Big Data and
what is its importance?
Big Data is a term related to
large and complex data sets. Big Data is required in order to manage and
perform different operation on a wide set of data.
8. What is Apache Spark and what are the
benefits of Spark over MapReduce?
Spark is really fast. If run in-memory
it is 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce.
In Hadoop MapReduce, you write
many MapReduce jobs and then tie these jobs together using Oozie/shell script. This
mechanism is very time consuming and MapReduce tasks have heavy latency.
Between two consecutive MapReduce jobs, the data has to be written to HDFS and
read from HDFS. This is time-consuming. In case of Spark, this is avoided using
RDDs and utilizing memory (RAM). And quite often, translating the output of one
MapReduce job into the input of another MapReduce job might require writing
another code because Oozie may not suffice.
9.What are the downsides of Spark?
Spark utilizes the memory. So, in
a shared environment, it might consume little more memory for longer durations.
The developer has to be careful.
A casual developer might make following mistakes:
·
She may end up running everything on the local
node instead of distributing work over to the cluster.
·
She might hit some web service too many times by
the way of using multiple clusters.
10. On which all platform can
Apache Spark run?
Spark can run on the following
platforms:
• YARN
(Hadoop): Since yarn can handle any kind of workload, the spark can run on
Yarn. Though there are two modes of execution. One in which the Spark driver is
executed inside the container on node and second in which the Spark driver is
executed on the client machine. This is the most common way of using Spark.
• Apache
Mesos: Mesos is an open source good upcoming resource manager. Spark can run on
Mesos.
11. What are the various
programming languages supported by Spark?
Though Spark is written in Scala,
it lets the users’ code in various languages such as:
• Scala
• Java
• Python
• R
(Using SparkR)
• SQL
(Using SparkSQL)
Also, by the way of piping the
data via other commands, we should be able to use all kinds of programming
languages or binaries.
11.What are the various modes in
which Spark runs on YARN? (Local vs. Client vs. Cluster Mode)
Apache Spark has two basic parts:
1. Spark Driver: Which controls what to execute where
2. Executor: Which actually executes the logic
While running Spark on YARN,
though it is very obvious that executor will run inside containers, the driver
could be run either on the machine which user is using or inside one of the
containers. The first one is known as Yarn client mode while second is known as
Cluster-Mode. The following diagrams should give you a good idea:
YARN client mode: The driver is
running on the machine from which client is connected
12.What are the various storages
from which Spark can read data?
Spark has been designed to
process data from various sources. So, whether you want to process data stored
in HDFS, Cassandra, EC2, Hive, HBase, and Alluxio (previously Tachyon). Also,
it can read data from any system that supports any Hadoop data source.
13.While processing data from HDFS,
does it execute code near data?
Yes, it does in most cases. It
creates the executors near the nodes that contain data.
And Answers
Here are the top Apache Spark
interview questions and answers. There is a massive growth in the big data
space, and job opportunities are skyrocketing, making this the perfect time to
launch your career in this space.
Our experts have curated these
questions to give you an idea of the type of questions which may be asked in an
interview. Hope these Apache Spark interview questions and answers guide will
help you in getting prepared for your next interview.
14.What is Apache Spark and what are the benefits
of Spark over MapReduce?
Spark is really fast. If run
in-memory it is 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce.
In Hadoop MapReduce, you write
many MapReduce jobs and then tie these jobs together using Oozie/shell script.
This mechanism is very time consuming and MapReduce tasks have heavy latency.
Between two consecutive MapReduce jobs, the data has to be written to HDFS and
read from HDFS. This is time-consuming. In case of Spark, this is avoided using
RDDs and utilizing memory (RAM). And quite often, translating the output of one
MapReduce job into the input of another MapReduce job might require writing
another code because Oozie may not suffice.
In Spark, you can basically do
everything from single code or console (PySpark or Scala console) and get the
results immediately. Switching between ‘Running something on cluster’ and
‘doing something locally’ is fairly easy and straightforward. This also leads
to less context switch of the developer and more productivity.
Spark kind of equals to MapReduce
and Oozie put together.
Watch this video to learn more
about benefits of using Apache Spark over MapReduce.
15.Is there any point of learning MapReduce,
then?
MapReduce is a paradigm used by
many big data tools including Spark. So, understanding the MapReduce paradigm and
how to convert a problem into series of MapReduce tasks is very important.
Many organizations have already
written a lot of code in MapReduce. For legacy reasons, it is required.
Almost, every other tool such as
Hive or Pig converts its query into MapReduce phases. If you understand the
MapReduce then you will be able to optimize your queries better.
16.What are the downsides of Spark?
Spark utilizes the memory. So, in
a shared environment, it might consume little more memory for longer durations.
The developer has to be careful.
A casual developer might make following mistakes:
She may end up running everything
on the local node instead of distributing work over to the cluster.
She might hit some web service
too many times by the way of using multiple clusters.
The first problem is well tackled
by Hadoop MapReduce paradigm as it ensures that the data your code is churning
is fairly small a point of time thus you can make a mistake of trying to handle
whole data on a single node.
The second mistake is possible in
MapReduce too. While writing MapReduce, a user may hit a service from inside of
map() or reduce() too many times. This overloading of service is also possible
while using Spark.
Learn Spark From Experts! Enroll
Now>>
17. Explain in brief what is the architecture of
Spark?
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
Architecture
Spark Interview Questions – Spark
Architecture
At the architecture level, from a
macro perspective, the Spark might look like this:
Spark Architecture
5) Interactive Shells or Job
Submission Layer
4) API Binding: Python, Java,
Scala, R, SQL
3) Libraries: MLLib, GraphX,
Spark Streaming
2) Spark Core (RDD &
Operations on it)
1) Spark Driver -> Executor
Scheduler or Resource Manager
At the bottom is the resource
manager. This resource manager could be external such YARN or Mesos. Or it
could be internal if the Spark is running in standalone mode. The role of this
layer is to provide a playground in which the program can run distributively. For
example, YARN (Yet Another Resource Manager) would create application master,
executors for any process.
1) Spark Driver -> Executor:
One level above scheduler is the
actual code by the Spark which talks to the scheduler to execute. This piece of
code does the real work of execution. The Spark Driver that would run inside
the application master is part of this layer. Spark Driver dictates what to
execute and executor executes the logic.
2) Spark Core (RDD &
Operations on it):
Spark Core is the layer which
provides maximum functionality. This layer provides abstract concepts such as
RDD and the execution of the transformation and actions.
3) Libraries: MLLib,, GraphX,
Spark Streaming, Dataframes:
The additional vertical wise
functionalities on top of Spark Core is provided by various libraries such as
MLLib, Spark Streaming, GraphX, Dataframes or SparkSQL etc.
4) API Bindings are internally
calling the same API from different languages.
5) Interactive Shells or Job
Submission Layer:
The job submission APIs provide a
way to submit bundled code. It also provides interactive programs (PySpark,
SparkR etc.) that are also called REPL or Read-Eval-Print-Loop to process data
interactively.
Watch this video to learn more
about Spark architecture.
18.On which all platform can Apache
Spark run?
.Spark can run on the following
platforms:
YARN (Hadoop): Since yarn can
handle any kind of workload, the spark can run on Yarn. Though there are two
modes of execution. One in which the Spark driver is executed inside the
container on node and second in which the Spark driver is executed on the
client machine. This is the most common way of using Spark.
Apache Mesos: Mesos is an open
source good upcoming resource manager. Spark can run on Mesos.
EC2: If you do not want to manage
the hardware by yourself, you can run the Spark on top of Amazon EC2. This
makes spark suitable for various organizations.
Standalone: If you have no
resource manager installed in your organization, you can use the standalone
way. Basically, Spark provides its own resource manager. All you have to do is
install Spark on all nodes in a cluster, inform each node about all nodes and
start the cluster. It starts communicating with each other and run.
19.What are the various programming
languages supported by Spark?
Though Spark is written in Scala,
it lets the users code in various languages such as:
Scala
Java
Python
R (Using SparkR)
SQL (Using SparkSQL)
Also, by the way of piping the
data via other commands, we should be able to use all kinds of programming
languages or binaries.
Learn Scala For Free>>
What are the various modes in
which Spark runs on YARN? (Local vs Client vs Cluster Mode)
Apache Spark has two basic parts:
Spark Driver: Which controls what
to execute where
Executor: Which actually executes
the logic
While running Spark on YARN,
though it is very obvious that executor will run inside containers, the driver
could be run either on the machine which user is using or inside one of the
containers. The first one is known as Yarn client mode while second is known as
Cluster-Mode. The following diagrams should give you a good idea:
YARN client mode: The driver is
running on the machine from which client is connected
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
RDD Client Mode
Spark Interview Questions – Spark
RDD Client Mode
YARN cluster mode: The driver
runs inside the cluster.
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
RDD Cluster Mode
Spark Interview Questions – Spark
RDD Cluster-Mode
Watch this video to learn more
about cluster mode.
Local mode: It is only for the
case when you do not want to use a cluster and instead want to run everything
on a single machine. So Driver Application and Spark Application are both on
the same machine as the user.
Watch this video to learn more
about local mode.
20.What are the various storages from which Spark
can read data?
Spark has been designed to
process data from various sources. So, whether you want to process data stored
in HDFS, Cassandra, EC2, Hive, HBase, and Alluxio (previously Tachyon). Also,
it can read data from any system that supports any Hadoop data source.
While processing data from HDFS,
does it execute code near data?
Yes, it does in most cases. It
creates the executors near the nodes that contain data.
21.What are the various libraries
available on top of Apache Spark?
Spark powers a stack of libraries
including SQL and Data Frames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX, and Spark
Streaming. You can combine these libraries seamlessly in the same application.
MLlib: It is machine learning
library provided by Spark. It basically has all the algorithms that internal
are wired to use Spark Core (RDD Operations) and the data structures required.
For example, it provides ways to translate the Matrix into RDD and
recommendation algorithms into sequences of transformations and actions. MLLib
provides the machine learning algorithms that can run parallel on many
computers.
GraphX: GraphX provides libraries
which help in manipulating huge graph data structures. It converts graphs into
RDD internally. Various algorithms such PageRank on graphs are internally
converted into operations on RDD.
Spark Streaming: It is a very
simple library that listens on unbounded data sets or the datasets where data
is continuously flowing. The processing pauses and waits for data to come if
the source isn’t providing data. This library converts the incoming data
streaming into RDDs for the “n” seconds collected data aka batch of data and
then run the provided operations on the RDDs.
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
Libraries
Spark Interview Questions – Spark
Libraries
22. Does Spark provide the storage layer too?
No, it doesn’t provide storage
layer but it lets you use many data sources. It provides the ability to read
from almost every popular file systems such as HDFS, Cassandra, Hive, HBase,
SQL servers.
23. Where does Spark Driver run on Yarn?
If you are submitting a job with
–master client, the Spark driver runs on the client’s machine. If you are
submitting a job with –master yarn-cluster, the Spark driver would run inside a
YARN container.
24.To use Spark on an existing
Hadoop Cluster, do we need to install Spark on all nodes of Hadoop?
And Answers
Here are the top Apache Spark
interview questions and answers. There is a massive growth in the big data
space, and job opportunities are skyrocketing, making this the perfect time to
launch your career in this space.
Our experts have curated these
questions to give you an idea of the type of questions which may be asked in an
interview. Hope these Apache Spark interview questions and answers guide will
help you in getting prepared for your next interview.
25. What is Apache Spark and what
are the benefits of Spark over MapReduce?
Spark is really fast. If run
in-memory it is 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce.
In Hadoop MapReduce, you write
many MapReduce jobs and then tie these jobs together using Oozie/shell script.
This mechanism is very time consuming and MapReduce tasks have heavy latency.
Between two consecutive MapReduce jobs, the data has to be written to HDFS and
read from HDFS. This is time-consuming. In case of Spark, this is avoided using
RDDs and utilizing memory (RAM). And quite often, translating the output of one
MapReduce job into the input of another MapReduce job might require writing
another code because Oozie may not suffice.
In Spark, you can basically do
everything from single code or console (PySpark or Scala console) and get the results
immediately. Switching between ‘Running something on cluster’ and ‘doing
something locally’ is fairly easy and straightforward. This also leads to less
context switch of the developer and more productivity.
Spark kind of equals to Map Reduce
and Ozzie put together.
Watch this video to learn more
about benefits of using Apache Spark over Map Reduce.
26.Is there any point of learning
Map Reduce, then?
Map Reduce is a paradigm used by
many big data tools including Spark. So, understanding the Map Reduce paradigm
and how to convert a problem into series of Map Reduce tasks is very important.
Many organizations have already
written a lot of code in Map-reduce. For legacy reasons, it is required.
Almost, every other tool such as
Hive or Pig converts its query into Map Reduce phases. If you understand the
Map Reduce then you will be able to optimize your queries better.
27.What are the downsides of Spark?
Spark utilizes the memory. So, in
a shared environment, it might consume little more memory for longer duration.
The developer has to be careful.
A casual developer might make following mistakes:
She may end up running everything
on the local node instead of distributing work over to the cluster.
She might hit some web service
too many times by the way of using multiple clusters.
The first problem is well tackled
by Hadoop MapReduce paradigm as it ensures that the data your code is churning
is fairly small a point of time thus you can make a mistake of trying to handle
whole data on a single node.
The second mistake is possible in
Map Reduce too. While writing MapReduce, a user may hit a service from inside of
map() or reduce() too many times. This overloading of service is also possible
while using Spark.
28.Explain in brief what is the
architecture of Spark?
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
Architecture
At the architecture level, from a
macro perspective, the Spark might look like this:
Spark Architecture
5) Interactive Shells or Job
Submission Layer
4) API Binding: Python, Java,
Scala, R, SQL
3) Libraries: MLLib, GraphX,
Spark Streaming
2) Spark Core (RDD &
Operations on it)
1) Spark Driver -> Executor
0) Scheduler or Resource Manager
0) Scheduler or Resource Manager:
At the bottom is the resource
manager. This resource manager could be external such YARN or Mesos. Or it
could be internal if the Spark is running in standalone mode. The role of this
layer is to provide a playground in which the program can run distributively.
For example, YARN (Yet Another Resource Manager) would create application
master, executors for any process.
1) Spark Driver -> Executor:
One level above scheduler is the
actual code by the Spark which talks to the scheduler to execute. This piece of
code does the real work of execution. The Spark Driver that would run inside
the application master is part of this layer. Spark Driver dictates what to
execute and executor executes the logic.
Spark Interview Questions - Spark
Driver and Executors
Spark Interview Questions – Spark
Driver and Executors
2) Spark Core (RDD &
Operations on it):
Spark Core is the layer which
provides maximum functionality. This layer provides abstract concepts such as
RDD and the execution of the transformation and actions.
3) Libraries: MLLib,, GraphX,
Spark Streaming, Dataframes:
The additional vertical wise
functionalities on top of Spark Core is provided by various libraries such as
MLLib, Spark Streaming, GraphX, Dataframes or SparkSQL etc.
4) API Bindings are internally
calling the same API from different languages.
5) Interactive Shells or Job
Submission Layer:
The job submission APIs provide a
way to submit bundled code. It also provides interactive programs (PySpark,
SparkR etc.) that are also called REPL or Read-Eval-Print-Loop to process data
interactively.
Watch this video to learn more
about Spark architecture.
29. What is spark Context?
Spark Context is the entry point
to Spark. Using spark Context you create RDDs which provided various ways of
churning data.
What is DAG – Directed Acyclic
Graph?
Directed Acyclic Graph – DAG is a
graph data structure having edges which are directional and do not have any
loops or cycles
DAG is a way of representing
dependencies between objects. It is widely used in computing. The examples
where it is used in computing are:
Build tools such Apache Ant, Apache
Maven, make, sbt
Tasks Dependencies in project
management – Microsoft Project
The data model of Git
30.What is broadcast variable?
Quite often we have to send
certain data such as a machine learning model to every node. The most efficient
way of sending the data to all of the nodes is by the use of broadcast
variables.
LEARN LATEST INTERVIEW QUESTION & ANSWERS
31.Big Data Certification?
A Big Data certification can
offer your career a big boost, whether you’re just getting started or you’re a
seasoned professional. If you’re new to the field, a Big Data certification
will get you trained so you can make the transition and land that first job.
Those types of certifications can range from the very specific, such as an
introduction to Big Data and Hadoop, to wide-ranging, like a Big Data and Data
Science Master’s program that earns you several different certifications as
part of the learning path.
32. Top Big Data Certification
Choices?
Once you realize a certification
is a worthwhile investment in your career, your next step is choosing the type
of certification and the provider. When it comes to Big Data certification,
your choices are almost as numerous as the many areas of study in Big Data. In
addition to education providers who offer certifications, the software
companies that create the technology driving Big Data also offer
certifications.
33.The top 7 data analytics and big
data certifications ?
Certification of Professional
Achievement in Data Sciences
Certified Analytics Professional
Cloudera Certified Associate
(CCA) Data Analyst
EMC Proven Professional Data
Scientist Associate (EMCDSA)
MapR Certified Data Analyst
Microsoft Certified Solutions
Expert (MCSE): Data Management and Analytics
SAS Certified Data Scientist
Using SAS 9
34.Certification of Professional
Achievement in Data Sciences ?
The Certification of Professional
Achievement in Data Sciences is a non-degree program intended to develop
facility with foundational data science skills. The program consists of four
courses: Algorithms for Data Science, Probability & Statistics, Machine
Learning for Data Science, and Exploratory Data Analysis and Visualization.
35.Certified Analytics Professional ?
The Certified Analytics
Professional (CAP) credential is a general analytics certification that
certifies end-to-end understanding of the analytics process, from framing
business and analytic problems to acquiring data, methodology, model building,
deployment and model lifecycle management. It requires completion of the CAP
exam and adherence to the CAP Code of Ethics.
36.EMC Proven Professional Data
Scientist Associate (EMCDSA)?
The EMCDSA certification
demonstrates an individual's ability to participate and contribute as a data
science team member on big data projects. It includes deploying the data
analytics lifecycle, reframing a business challenge as an analytics challenge,
applying analytic techniques and tools to analyse big data and create
statistical models, selecting the appropriate data visualizations and more.
37.MapR Certified Data Analyst ?
The MapR Certified Data Analyst
credential validates an individual's ability to perform analytics on large
datasets using a variety of tools, including Apache Hive, Apache Pig and Apache
Drill. The exam tests the ability to perform typical ETL tasks to manipulate
data to perform queries. Questions touch on existing SQL queries, including
debugging malformed queries from a given code snippet, choosing the correct
query functions to produce a desired result, and typical troubleshooting tasks.
The exam consists of 50-60 questions in a two-hour proctored session.
38.SAS Certified Data Scientist
Using SAS 9 ?
The SAS Certified Data Scientist
Using SAS 9 credential demonstrates that individuals can manipulate and gain
insights from big data with a variety of SAS and open source tools, make
business recommendations with complex learning models, and then deploy models
at scale using the SAS environment. The certification requires passing five
exams that include multiple choice, short answer, and interactive questions (in
a simulated SAS environment)
39.Cloudera Certified Associate (CCA) Data Analyst ?
A SQL developer who earns the CCA Data Analyst certification demonstrates core analyst skills to load, transform and model Hadoop data to define relationships and extract meaningful results from the raw output. It requires passing the CCA Data Analyst Exam (CCA159), a remote-proctored set of eight to 12 performance-based, hands-on tasks on a CDH 5 cluster.
40.What is accumulator?
An accumulator is a good way to continuously gather data from a Spark process such as the progress of an application. The accumulator receives data from all the nodes in parallel efficiently. Therefore, only the operations in order of operands don’t matter are valid accumulators. Such functions are generally known as associative operations.
Say I have a huge list of numbers in RDD(say myRDD). And I wrote the following code to compute average:
1. Def. myAvg(x, y):
2. Return (x+y)/2.0;
3. Avg = myrdd.reduce (myAvg);
 Hadoop is an appropriated File System for preparing a huge measure of information in a dispersed Environment. Indeed, even the information is prepared all the while there are a few impediments. Tell us the downsides of HDFS.
Hadoop is an appropriated File System for preparing a huge measure of information in a dispersed Environment. Indeed, even the information is prepared all the while there are a few impediments. Tell us the downsides of HDFS.



